Translation and transcription are two of the most important words for global audiences. The former translates a text or piece of media into a different language, whereas the latter takes speech, such as from video, audio, or conversations and interviews, and turns them into written text.
The two concepts may seem very simple, but there are some major differences between them that anybody working in multimedia and multilingual environments needs to be aware of.
This transcription vs translation comparison will provide you with the information required to choose between the two. You might discover that depending on the environment you work in, you may have a need for both. So, what’s the difference between transcription and translation? Let’s get to it.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Both transcription and translation are crucial for reaching a wider audience, making media more accessible, and growing businesses.
- Transcription involves converting spoken words into written text, whereas translation involves taking that written text and translating it into one or more languages.
- There are many artificial intelligence tools that can do both with astounding accuracy, such as Sonix, which has a 99% transcription accuracy rate.
Transcription vs Translation: What Are the Differences?
Transcription takes spoken words from audio and video files and from lectures, meetings, and conversations and converts them to written text in the original language. Translation involves taking speech or text in one language and converting it to one or many others while keeping the contextual meaning and factual information as accurate as possible.
Although both can be done manually by trained professionals, AI-based tools are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use.
Here’s a direct comparison of the two in tabular form before we move on to a longer explanation.
| Category | Translation | Transcription |
| Definition | Converting text or speech from one language to another. | Converting spoken language into written or electronic text format. |
| Primary Objective | Facilitate communication across different language speakers. | Create a readable and accurate record of verbal communications. |
| Processes Involved | Understanding of source and target languages, cultural nuances, context, and idiomatic expressions. | Listening to audio or video recordings, typing, editing for clarity or verbatim accuracy. |
| Skills Required | Linguistic expertise in both source and target languages, cultural sensitivity, subject matter knowledge. | Excellent listening skills, fast and accurate typing, understanding of the spoken content’s context. |
| Typical Contexts | Literary works, legal documents, medical records, websites, and technical manuals. | Legal proceedings, medical transcriptions, media production, corporate meetings, and academic research. |
| End Product | Text in a different language that accurately conveys the original message and context. | Written document that accurately captures the spoken words and possibly non-verbal cues. |
| Challenges | Navigating linguistic nuances, idiomatic expressions, cultural context, and maintaining tone and style. | Ensuring accuracy with unclear audio, speaker accents, technical terminology, and background noise. |
What is Transcription?
Transcription is the process of taking spoken words, whether from a meeting, lecture, conversation, audio file, or video file, and converting them into a written format in the same language.
This is a very important practice in various contexts and fields, as it helps ensure that speech-based information is precisely captured, recorded, and made easily accessible for future analysis and reference.
- There are many contexts where transcription can be very useful, such as for legal proceedings. Transcriptions are crucial in the legal world, as they ensure that words spoken in legal settings are precisely captured for further review.
- Transcriptions are used in media production to convert audio content from interviews, films, and television shows into text, often in the form of scripts. These transcripts may also be used for post-production and editing purposes.
- Transcriptions may then also be used to create closed captions and subtitles to make media more accessible to a wider range of people.
- Another area where accurate transcription is important is for corporate meetings, where minutes need to be accurately recorded, and action items, discussions, and records of decisions need to be kept in great detail and accuracy.
- There are also other fields that often use transcription, such as in the healthcare field, where voice-recorded reports are converted into written format, as well as in the academic field, where lectures and interviews are converted into text format for future reference.
Benefits of Transcription
While it may seem like a lot of trouble for most people, there are a few key benefits of transcribing your video/audio into text or captions.
Record Keeping
As far as the benefits are concerned, transcriptions often make it much easier to analyze audio and video files, as well as speech, as accurate transcriptions allow for future reference and review.
This is great for organizations like law firms that have a lot of video/audio data on hand and want to make it easier to review at a later date, as it can be quite a pain to find a specific part of a clip every time you need to double-check something. Transcripts with timestamps and sentiment analysis can provide you with the exact information you need when you need it. It’s all about making information easier to access.
Wider Accessibility
Speaking of movies, video, and audio content, transcription also makes all of these types of content much more accessible to a wider range of people, particularly those who are hard of hearing or deaf. Transcriptions can be converted into closed captions, allowing those with auditory impairments to enjoy video and audio content.
SEO Benefits
Although not too closely related to today’s topic and despite being irrelevant for most, it’s still a benefit worth considering. The search crawlers used by Google can’t parse audio/video files. So, if you’re adding them to your site and your content, Google has no way to actually know what the video contains.
This is where transcriptions come in. They have the added benefit of search engine optimization improvement. By adding transcriptions, you’re telling search engines what the video is about, effectively increasing your visibility and the chances of ranking higher on the first page.
Types of Transcription
There is more than one type of transcription, three to be precise, and each serves a slightly different purpose. Let’s break them down below.
Verbatim Transcription
Verbatim transcription is a process that involves transcribing everything that is said down to the exact detail, including sounds, spoken words, any utterances, any forms of nonverbal communication, and anything else that may take place in the conversation, meeting, or media file. This is most often used in qualitative research and for legal proceedings.
Edited Transcription
Next, we have edited transcription, which has the purpose of creating a more readable and clear transcription. Edited transcription aims to correct grammatical mistakes, omit nonverbal cues, and get rid of irrelevant information and filler words. Professional settings, mainly corporations, often use this type of transcription.
Intelligent Transcription
Intelligent transcription, also known as clean transcription, aims to take the meaning of the speaker and convey it in a clear as possible manner while ensuring that the text is concise, clear, and free of grammatical errors. It is often seen as the middle ground between verbatim transcription and edited transcription.
What is Translation?
Translation involves taking speech or text in one language and converting it into one or many others while ensuring that the original context, intent, tone, message, and factual information is preserved and conveyed to a target audience in an accurate manner.
Translation is a very nuanced and complex process that requires an intimate understanding of both the source and target languages, subject matter expertise, and cultural sensitivity. Translation is extremely important for bridging gaps between speakers of different languages, therefore allowing for cross-language trade, dialogue, and information accessibility.
Benefits of Translation
In terms of the benefits of translation, the number one benefit is accessibility. By taking written text or media files and converting them into multiple languages, people from all corners of the world can understand the content.
This is important in a variety of fields, whether video production and media, government services, education, health care, the legal world, and more. It’s about allowing a wider audience to access the same information in spite of language barriers.
This might not seem that important, but a great example emphasizing its effects would be MrBeast. Most of his content is in English on his main channel, which has 240 million plus subscribers. While that is an impressive feat, a pretty neat accomplishment is his MrBeast en Espanol channel, which is a direct copy of his main channel with the videos translated word-for-word in Spanish.
That might not seem like a big deal, but his Spanish channel has over 25 million subscribers as well. That’s 25 million native speakers MrBeast wouldn’t be able to reach if he didn’t invest in translating his videos.
Types of Translation
While some might think that translation is simply converting text or media content from one language into another, there are a few types of translation to be aware of.
Literary Translation
One of the most common types of translation is literary translation, which involves taking plays, poems, and novels and translating them into other languages while maintaining accuracy, as well as the original tone and nuances.
Related to this is media translation, such as the translation of transcripts, captions, and subtitles for media content, therefore making television shows, movies, and even music more accessible to those who may be hard of hearing or seeing.
Website Translation
Website translation is another important type of translation to be aware of, one that’s particularly crucial for businesses looking to increase their global online outreach through the use of their websites and blogs. If businesses are to operate in various countries in today’s globally interconnected world, those businesses need to have websites that cater to those countries and their languages.
Technical Translation
Technical translation is another one to be aware of, one that involves taking technical specifications, user guides, and manuals, as well as other technical documents, and converting them into other languages with as much accuracy and precision as possible.
Judicial Translation
We then have judicial translation, otherwise known as legal translation, which involves taking legal documents, such as patents, statutes, contracts, and court rulings, and translating them into different languages, which requires an in-depth knowledge of legal workings and legal terminology.
Medical Translation
Medical translation is yet another important type of translation, as this involves translating consent forms, informational brochures, medical research, and patient records into various languages. This requires an in-depth understanding of medical terminology and is crucial for conveying information across various cultures in the medical field.
How to Use Sonix for Transcription and Translation
Now that we’ve established the basics of why it is important to transcribe and translate your videos, let’s talk about the how. Right now, Sonix is the most accurate artificial intelligence transcription and translation machine in the market.
Combined with its mind-boggling 99% accuracy rate, Sonix uses a variety of features such as speech recognition, advanced learning, sentiment analysis, and more, to provide transcripts as well as translations for hours’ worth of content in just a few minutes.
Using Sonix for both transcription and translation is extremely accurate, exceedingly simple, and cost-effective. Let’s take a quick look at how to do both.
Transcription
Creating a transcript of an audio or video file using Sonix is very simple, and all you have to do is follow the few steps listed below.
Step 1: Upload the File
Once you’ve logged into your Sonix account, upload your chosen file by clicking on the upload button. After clicking on the upload button, you can select a file from your computer. Once you’ve selected, Sonix will automatically upload it into its interface.
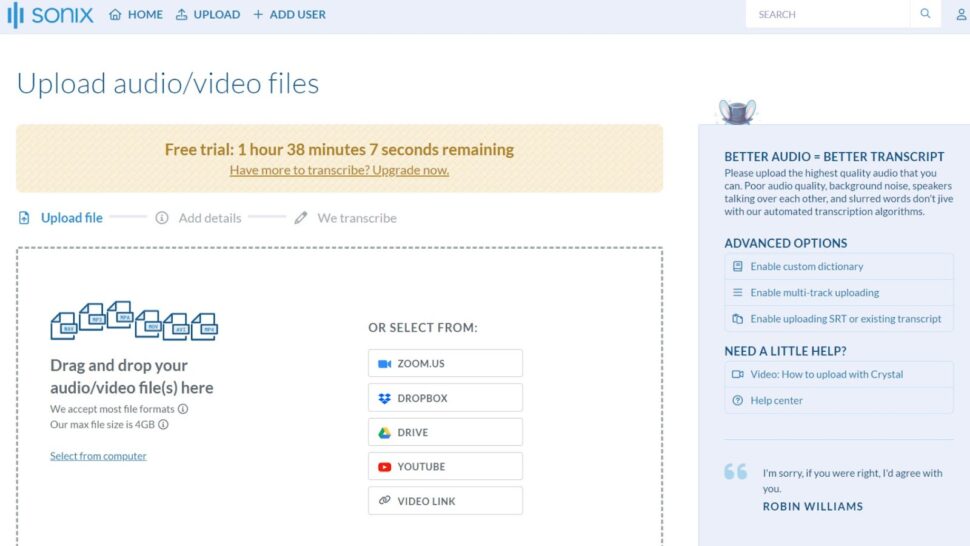
Step 2: Choose the Language and Allow Sonix to Transcribe
Once the media file has been chosen and uploaded, you’ll need to select the language that the original video or audio file is spoken in. Remember, Sonix supports over 39 different languages for transcription, so a lack of language choice should generally not be a problem.
What’s useful is that Sonix also has an automatic detection feature that can easily identify the language being spoken without the user having to manually input it. This is useful when you’re not sure what the source language is.
There are then various specific transcription options to choose from. After choosing your settings, click on the transcribe button. It should only take a few minutes for the process to be completed.
Step 3: Reviewing and Editing
Sonix features an accuracy rate of 99%, which means that you really shouldn’t have to do much reviewing or editing once the software has created a transcript. However, it is always recommended to give the file a bit of a read before using it.
Therefore, take a look at the quality report that the software generates, which informs you how good or bad the transcription in question is. You can then use the in-browser editor to examine the transcript for any mistakes and edits that need to be made.
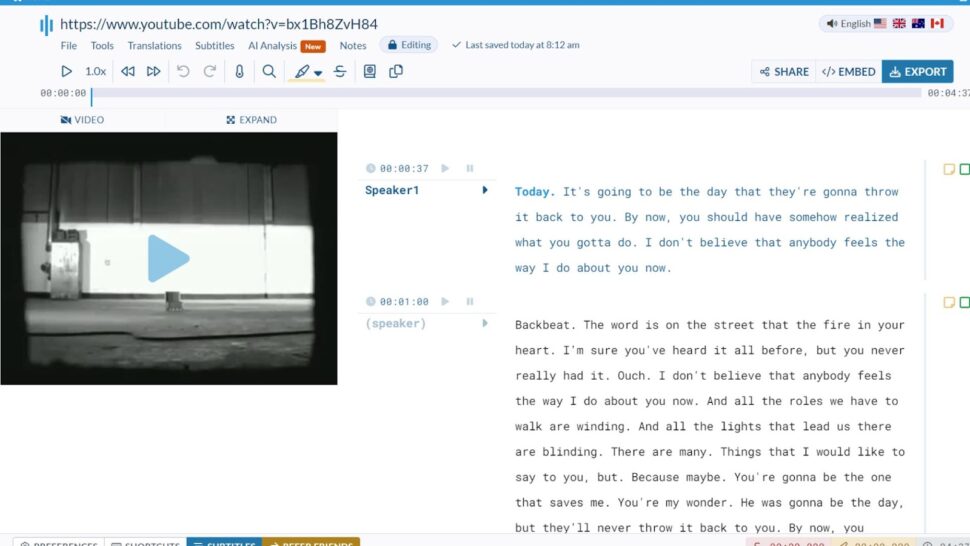
Translation
Although it might seem like translation is a totally separate process, Sonix makes it fast and easy. Sonix allows you to take that transcript that you just created in the steps above, and then translate it into one of nearly 40 languages through the automated translation function. Let’s take a look at how this works.

Within the online editor, you will see a translation function. Simply click on this function and select the language that you want the transcript to be translated into. Sonix will then use its advanced AI capabilities to create an accurate translation that contains the same factual information, tone, meaning, and nuances as the transcript did in the original language.
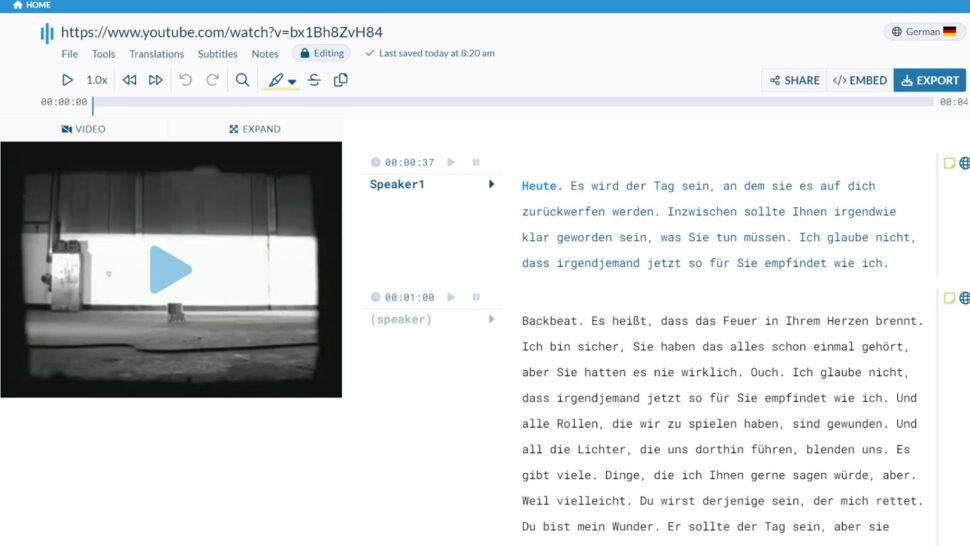
If you need a service that can produce highly accurate transcripts and translations for all of your media, meeting, lecture, and business needs, explore Sonix’s advanced capabilities!
Transcription vs Translation: How to Choose the Right One?
Although choosing between transcription and translation may seem difficult, there are really just a couple of main questions you need to ask yourself.
First, do you need a conversation, lecture, meeting, or any sort of video or audio content converted into written text? If the answer to this question is yes, then what you need is transcription.
The other question to ask yourself is, do you have a piece of written text, or in other words a transcript, that needs to be converted into one or many other languages? If the answer to this question is yes, then what you need is translation.
Final Thoughts
Knowing what sets apart transcriptions and translations is becoming increasingly important in this interconnected and globalized world. This is the case whether we are talking about business, media production, medicine, law, or any other industry.
Virtually every industry in the world at one time or another requires spoken content to be transcribed into a written format, and if that written text is to reach a wide target audience, then it needs to be translated into the various languages of those audiences.
The bottom line is that whether you need extremely accurate automatic transcriptions or translations, Sonix can do it both, and for a great price too.
If you’re looking to try out Sonix before making the purchase, there is a 30-minute free trial you can try out. No credit card required!
Transcription vs Translation: Frequently Asked Questions
Can Transcription and Translation Be Automated?
Yes, transcription and translation can be automated. For instance, Sonix uses machine learning, speech recognition, and other advanced features that allow audio and video files to be transcribed into written format with 99% accuracy. Companies like Sonix can also take those transcriptions and use advanced language models to create translations in nearly 40 languages.
Is Translation Easier Than Transcription?
Neither translation nor transcription is necessarily easier than the other. Translation requires knowledge of both languages, as well as idioms, cultural nuances, and structure, whereas transcription requires great attention to detail, familiarity with terminology, and a basic understanding of the underlying context. Both of these pose challenges in their own rights, making both fairly difficult to do manually.
Do Transcription and Translation Work Together?
As far as global content creation and communication are concerned, transcription and translation often work hand in hand. For example, to create accurate translations, companies like Sonix first take speech and convert it into a written transcript, which is then edited for clarity, and finally, this transcript can be translated into a language or languages of your choice.

